â‘ Hardness:
Due to the scientific synthesis of high-molecular polyurethane elastomer materials using iron rubber, the higher the hardness, the higher the modulus, the smaller the elongation, and the better the wear resistance and heat resistance. Well, in the range of minus 35 degrees Celsius to 100 degrees Celsius, and at a pressure of 60 to 70 MPa, the maximum sealing performance can be guaranteed.
The use of viscoelastic seals made of nitrile rubber is the most complete protection against damage caused by back pressure. In the range of minus 55 degrees Celsius to 100 degrees Celsius, and under a pressure of 21MPa, due to the rubber The seal is often in a compressed state, so the compression performance of the rubber seal must be considered. It not only achieves enhanced anti-climbing performance and low friction resistance, but also has good performance in dealing with special low-temperature oil, and can also be used in combination with Anti-wear Ring double-purpose retaining ring BRL type.
Sealing products made of polytetrafluoroethylene and nitrile rubber/PTFErubber; or seals made of nylon resin and nitrile rubber, which can be used in a wide range of applications with large pressure changes and fast sliding speeds According to the working condition, the input hydraulic pressure cutout is designed on the end face of the polytetrafluoroethylene ring to prevent penetration leakage. The maximum working temperature environment is minus 40 degrees Celsius to 160 degrees Celsius; the maximum working pressure is 50MPa.
oil seals,hydraulic oil seal,track link oil seal,TCV oil seal,O-ring Safe Seal Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.sprsealkits.com
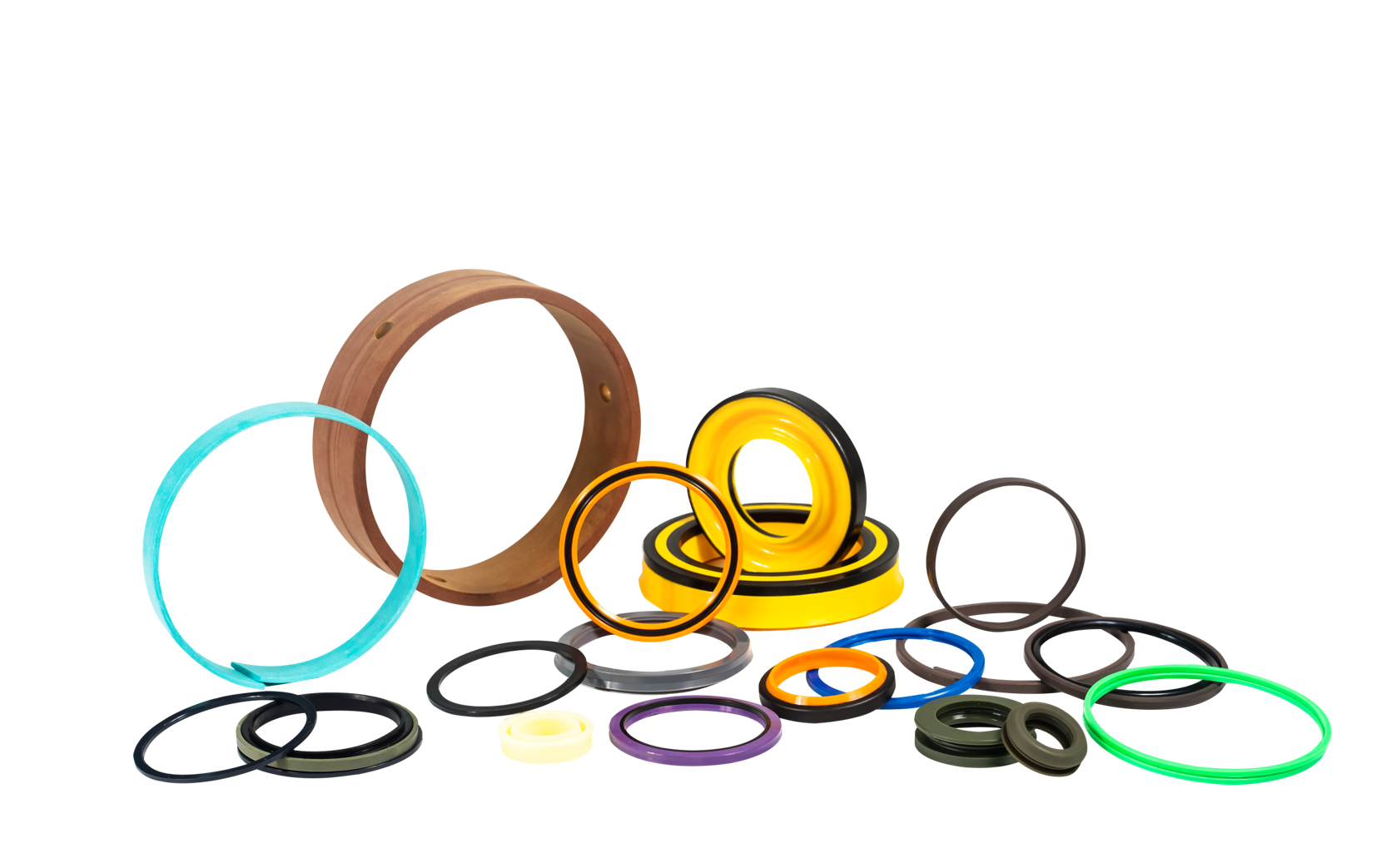
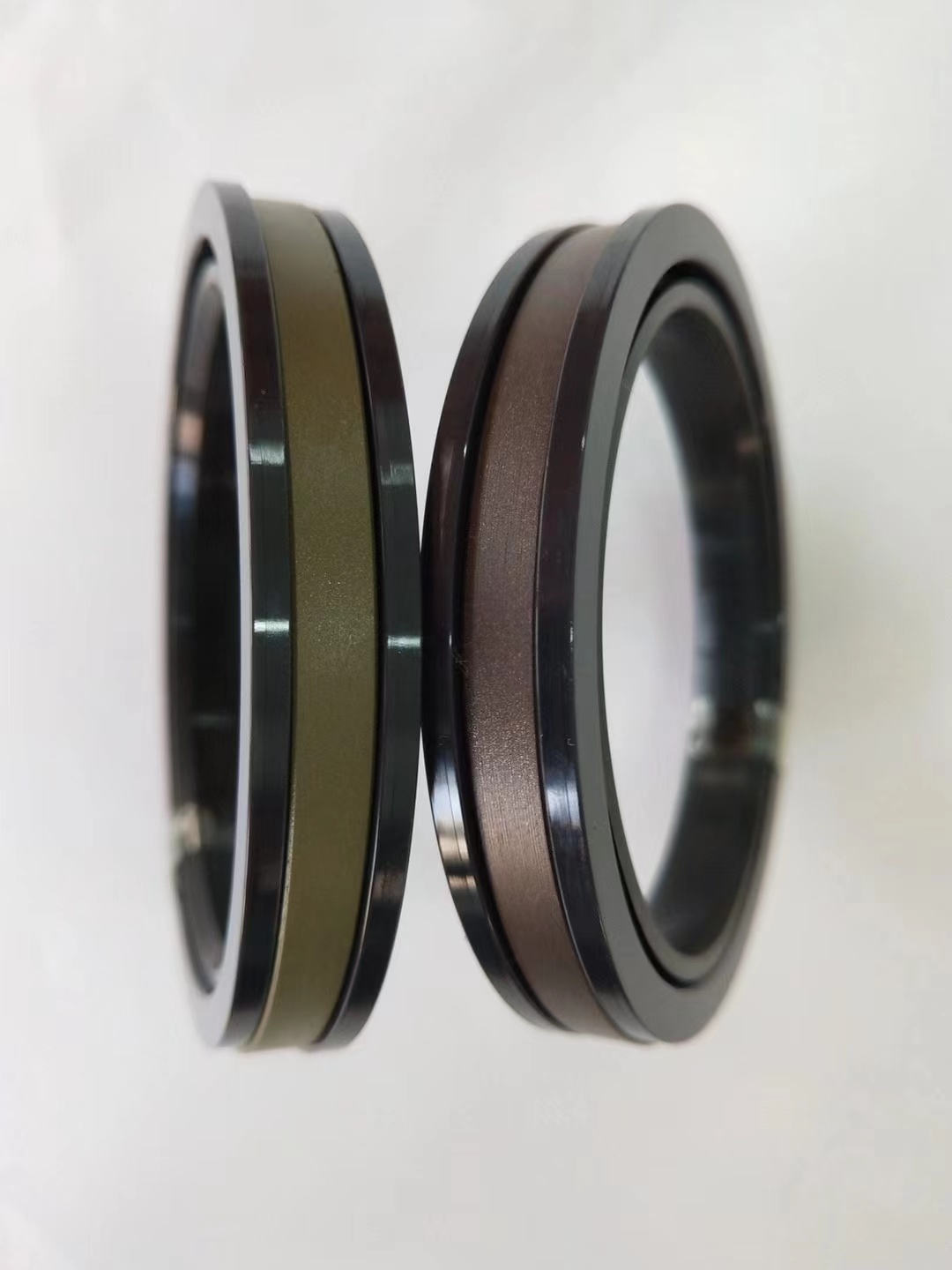


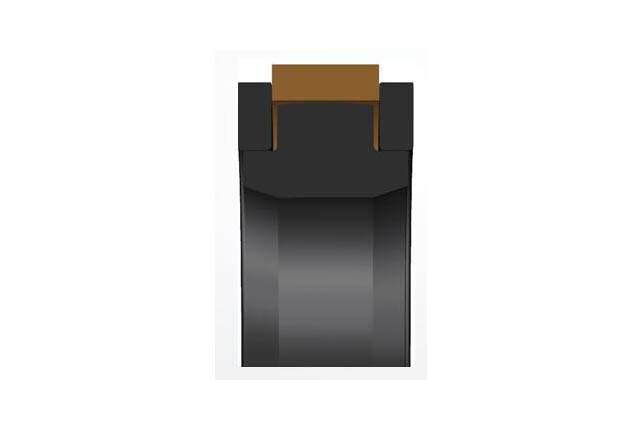
SPGW piston seal
Material:PTFE+rubber elastomer+reinforced modified nylon
Temperature:Nitrile rubber -40~100℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤50mpa
SPGO piston seal
Material:PTFE+rubber elastomer
Temperature:Nitrile rubber -40~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤35mpa
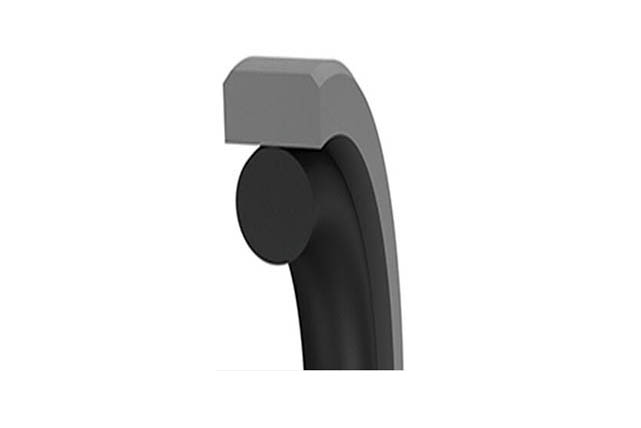

SRUV piston rod seal
Material:NBR+thermoplastic polyurethane
Temperature: -35`90℃
Speed:=0.5m/s
Pressure:≤40mpa
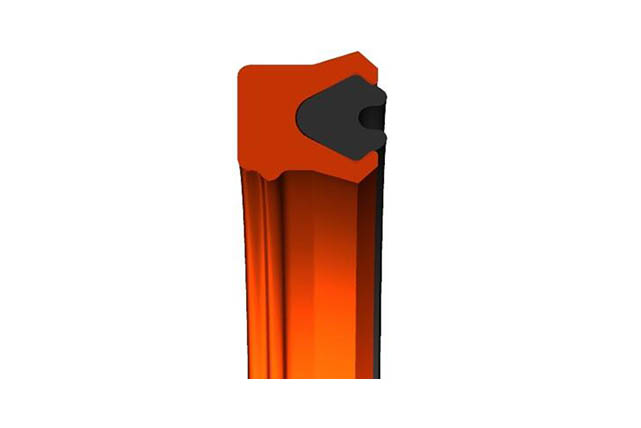

SRS piston rod seal
Material:PTFE+NBR
Temperature:-40~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤40mpa
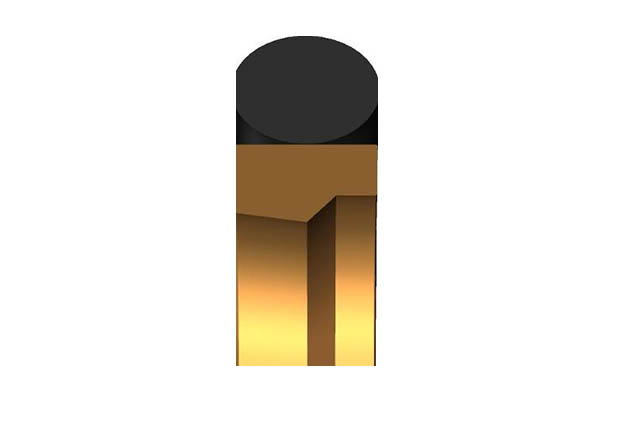

SRCB piston rod buffer seal
Material:Polyurethane+modified polyoxymethylene
Temperature: -35~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤50mpa
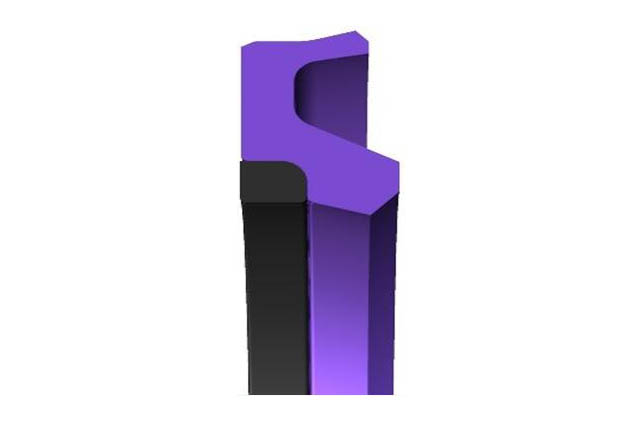

SRU piston rod seal
Material:Polyurethane
Temperature:-35~100℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤40mpa
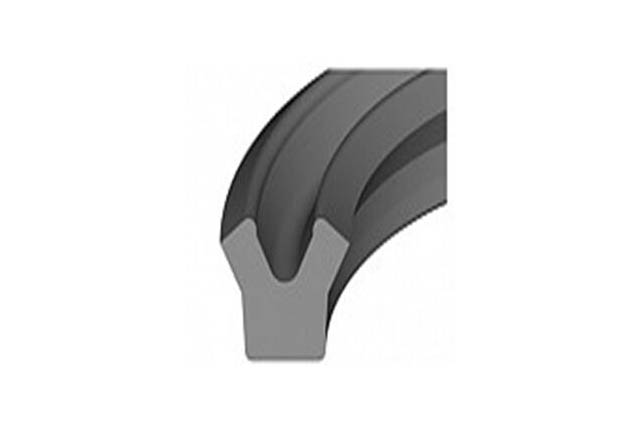

SRD iron case dust prevention
Material:Polyurethane+metal skeleton material
Temperature:-40~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
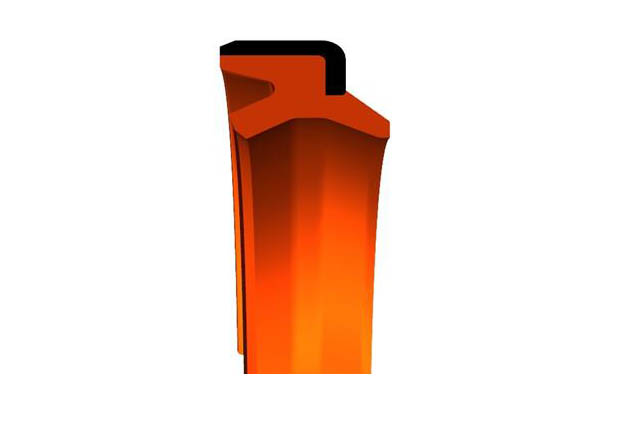

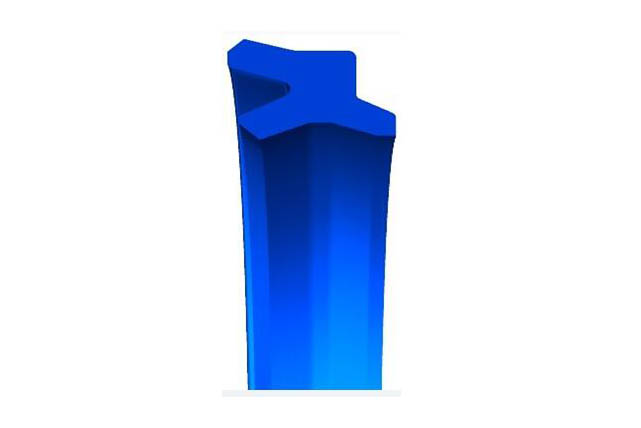
SRDI soft dustproof
Material:polyurethane
Temperature:-40~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/

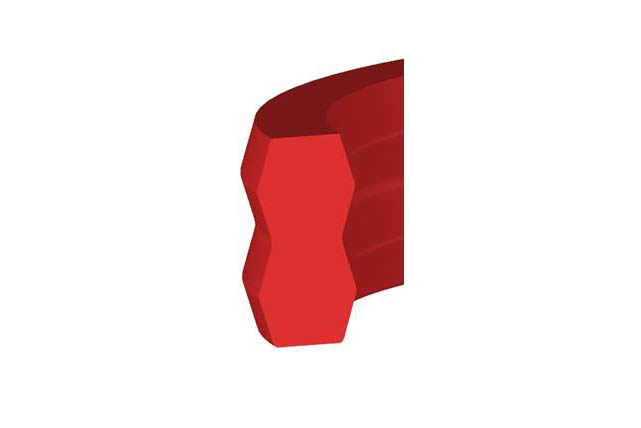
SDS Dumbbell Seal
Material:polyurethane
Temperature: -35~110℃
Speed:=0.5m/s
Pressure:≤50mpa
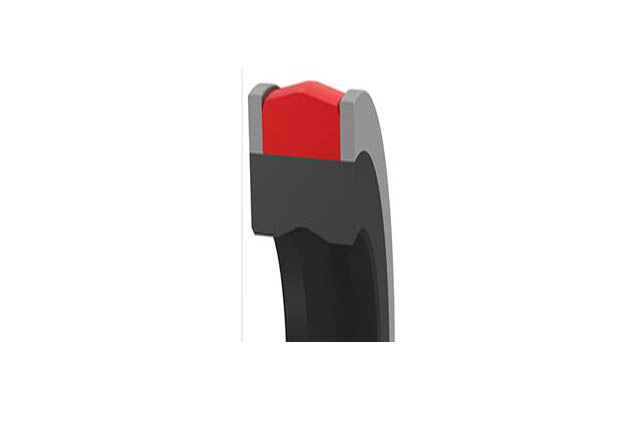
SPG piston combination seal
Temperature:
NBR+Polyurethane + Modified Polyoxymethylene
Temperature:-35`110℃
Speed:=0.3m/s
Pressure:≤70mpa

SRNL piston rod seal
Material
NBR+Polyurethane + Modified Polyoxymethylene
Temperature:-35`110℃
Speed:=0.3m/s
Pressure:≤70mpa
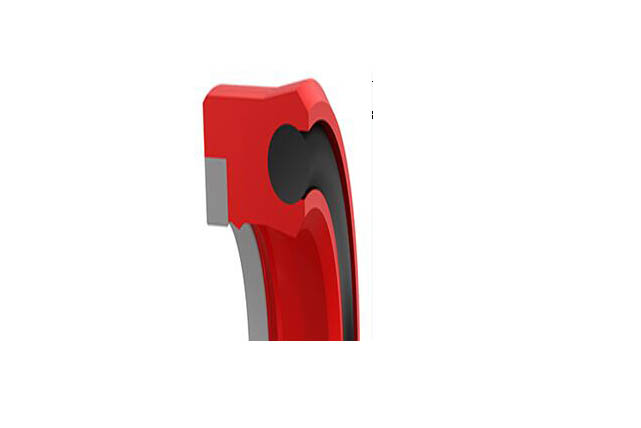

SRDF Piston Rod Seal
Material
Polyester rubber
Temperature:-40`100℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
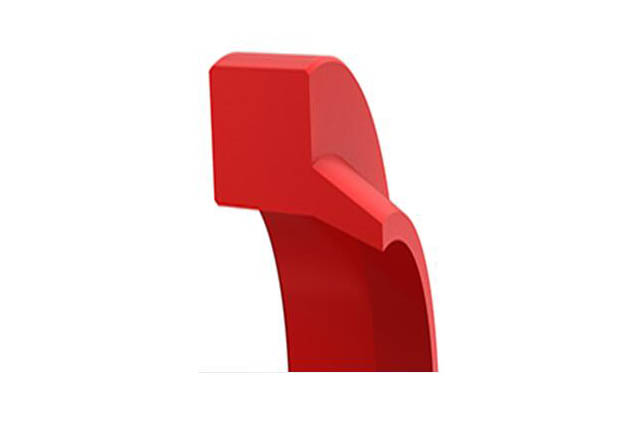

SDY Y-seal
Material:Polyurethane
Temperature:-35~110℃
Speed:=0.5m/s
Pressure:≤70mpa
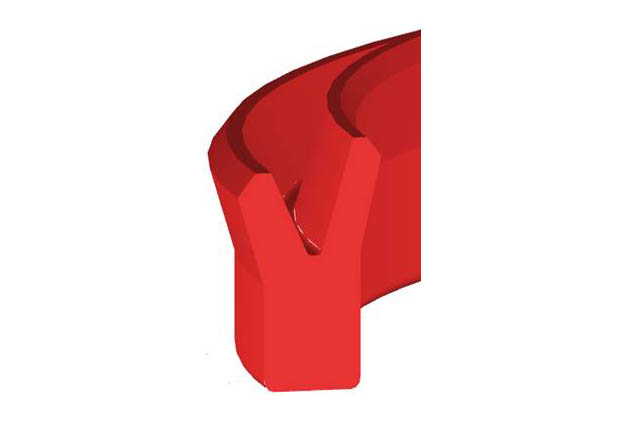

KZT anti fouling ring

SDS Steffel

Piston main oil seal

Characteristics, properties, reserves, compounds and main application areas of indium
Indium in the earth's crust is 0.1ppm (1ppm = 1μg / g, the same below), is a rare element, it can not form a separate mineral itself, scattered under natural conditions in other mineralized minerals. Indium thiophilic mainly the properties, especially some of the lead and zinc minerals thio stannate and antimony sulfide and higher salt content in the sulfide mineral. Indium is a major source of (iron) sphalerite, an amount of 100 ~ 1000ppm, copper ore has a content of indium. Since the indium content is low in minerals, it can not be used as an industrial raw material mining alone; timely indium content in the zinc most flash, still not independent as a mineral mining, only as a heavy non-ferrous metal smelting process Comprehensive utilization of raw material by-product recycling. Generally, in the comprehensive smelting of raw materials, as long as the content of indium reaches 200 ppm, it has a comprehensive recovery value.
Indium is a silver- white metal with a relative density of 7.3, a melting point of 156.6 ° C, and a boiling point of 2075 ° C; its softness, strong plasticity, and ductility, can be pressed into extremely thin sheets, but the tensile limit is low, The viscosity is large, so it is difficult to pull into a wire and is not conducive to cutting. The conductivity of indium is about 4/5 lower than that of copper, and its thermal expansion coefficient is almost double that of copper.
The chemical properties of indium are similar to those of iron, and together with zinc and iron, they form a homogeneous image. Indium can form monovalent, divalent, and trivalent compounds, but only trivalent compounds are stable, and only trivalent indium compounds are present in aqueous solution.
Indium oxide (In 2 O 3 ) is a yellow water-insoluble substance, and indium oxide can be obtained when indium is oxidized in air or calcined indium hydroxide. Indium oxide can be reduced to metal by hydrogen or carbon at 700 to 800 °C. The suboxide OO or In 2 O is an intermediate product at the time of reduction.
By reacting a base or a solution of ammonia and an indium salt, indium hydroxide can be obtained and precipitated as a white gel. Indium hydroxide starts to precipitate in a dilute solution having a pH of 3.5 to 3.7. When the concentration of indium increases, the pH of the precipitation of indium hydroxide can move toward the acid.
Indium trichloride is a colorless, volatile compound having a melting point of 586 ° C. However, it has begun to sublime at 450 ° C and is soluble in water.
Indium sulfate [In 2 (SO 4 ) 3 ] is one of the important salts of indium, and an anhydrous compound [In 2 (SO 4 ) 3 ·5H 2 O] is crystallized in a neutral solution at 100 to 120 ° C. It is also gradually dehydrated into an anhydrous compound. Indium sulfate is a white solid dissolved in water.
Indium and sulfur can form sulfides. If hydrogen sulfide is introduced into a neutral or weakly acidic indium acetate solution, yellow sulfide InS will precipitate.
At present, indium's mineral resources are mainly concentrated in the United States, Russia, Canada, South Africa and China, but other places such as Western Europe have refineries. According to USGS statistics, in 2000 the world's concentrate production volume was 220 tons, an increase of 3% over the previous year, and the world's storage (inventory) volume was about 5,600 tons. China's indium mineral resources are distributed in more than ten provinces, mainly concentrated in Guangxi, Yunnan, Guangdong and Inner Mongolia, accounting for 82.90% of the country's proven reserves, accounting for 84% of retained reserves. China's rare metal resources are relatively abundant. For example, indium resources have surpassed Canada, the United States, Russia, Peru and Japan, ranking first in the world. China's proven indium reserves exceed 10,000 tons, and the proven lead and zinc reserves are 35.73 million tons and 93.79 million tons respectively. The lead-zinc deposits in China have higher indium ratio than foreign countries, and the indium reserves associated with lead-zinc deposits are 8000. Tonne or so. [next]
The discovery of indium has been around for more than 100 years, and it took about 60 years to begin to apply it in industry and technology. At present, the field of application of indium has been significantly expanded, which is the result of an increasingly thorough understanding of the elements themselves and their compounds.
Indium is a versatile metal with low melting point, high boiling point, good conductivity, and the ability of oxides to form transparent conductive films. Its application range is expanding, especially in recent years, the use of indium is becoming more and more important. Widespread, especially in semiconductors, conductors, low melting point alloys, indium tin oxide, selenium indium copper thin film solar cells, fiber optic communications, atomic energy, television, anti-corrosion and other industrial applications have attracted more and more attention and attention. In addition to the above uses, the indium alloy can be made into a special alloy by using the low melting point of the indium alloy, which is used for the closed circuit protection device of the fire protection system and the thermal control device of the automatic control system. Because indium has strong corrosion resistance and light reflection ability, it can be made into a mirror on a warship or passenger ship, which can keep the light for a long time and can resist seawater corrosion. In addition, the use of indium as an anti-corrosion bearing, dental alloy, anti-corrosion decorative piece of steel and non-ferrous metals, plastic metallization and traditional jewelry monuments continues to grow.
About 70% of indium is used to make ITO (Indium Tin Oxide), which can be made into transparent electrodes for use on computers and other displays, especially LCD liquid crystal displays, which is the largest (terminal) user of ITO. The flat panel display is the "interface" between the human and the electronic world, which greatly promotes the development of mobile electronic devices, such as mobile phones and palmtop computers. The ITO film used in flat panel display is transparent to visible light, absorbs ultraviolet light, and reflects infrared light with good corrosion resistance as well as environmental and thermal stability.
The second largest area of ​​application for indium is solder, such as solder pastes and low melting (fusible) alloys, which have many applications. Indium is also used in the fabrication of semiconductor materials, which facilitate the development of high-speed digital networks to handle ever-increasing sound, image and digital transmission capacities.