What are the causes of frosting in the constant temperature and humidity test chamber refrigeration compressor? First, the compressor return air frosting indicates that the compressor return gas temperature is too low, then what will cause the compressor return gas temperature to be too low? It is known that if the same quality of refrigerant changes volume and pressure, the temperature will have different performance. If the liquid refrigerant absorbs more heat, the same quality of refrigerant will show high pressure, temperature and volume. Less heat, less pressure, temperature, and volume will be low. There are two problems that cause this problem: Second, due to less fluorine, the compressor returns to frost â—† Due to the low flow rate of the refrigerant, the refrigerant will start to expand from the first expandable space at the rear end of the throttle valve. Most of us see that the rear end of the expansion valve is often due to lack of fluorine or insufficient flow of the expansion valve. As a result, too little refrigerant expansion will not use all of the evaporator area, only a low temperature will be formed in the evaporator part, and some areas will be rapidly expanded due to the small amount of refrigerant, causing the local temperature to be too low, and the evaporator frosting will occur. â—† Due to the low amount of refrigerant, the evaporation pressure of the evaporator is low, resulting in low evaporation temperature, which will gradually lead to condensation of the evaporator to form a thermal insulation layer and transfer the expansion point to the compressor return air to cause the compressor to return to the air. All of the above points will show the evaporator frosting before the compressor returns to the air. Third, the cylinder head frosting (severe crankcase frosting), always caused by a large amount of wet steam or refrigerant suction into the compressor. The main reasons for this are: â—† When the liquid supply solenoid valve leaks or stops, the expansion valve is not closed tightly, resulting in a large amount of refrigerant liquid accumulated in the evaporator before starting. â—† When there are too many refrigerants in the system, the liquid level in the condenser is higher, the condensing heat exchange area is reduced, and the condensing pressure is increased, that is, the pressure before the expansion valve is increased, and the amount of refrigerant flowing into the evaporator is increased, and the liquid refrigerant is increased. It does not completely evaporate in the evaporator, so the compressor draws in wet steam, the cylinder hair is cold or even frosted, and may cause "liquid attack", and the evaporation pressure will also be high. How does a hydraulic press work? Pascal's Law in action Hydraulic Press Machine,Shop Press,Hydraulic Press For Sale,Workshop Press Jiangsu Hoston Machine Tools Co., Ltd. , https://www.haostonmachinetools.com
That is to say, if the compressor return air temperature is low, it generally shows that the return air pressure is low and the amount of refrigerant of the same volume is high. The root cause of this situation is that the refrigerant flowing through the evaporator cannot fully absorb itself and expand to the predetermined temperature. The amount of heat required for the pressure temperature value causes the temperature and pressure volume values ​​of the return air to be relatively low.
â—† Throttle valve liquid refrigerant supply is normal, but the evaporator can not normally absorb heat supply refrigerant expansion.
â—† The heat absorption of the evaporator is normal but the supply of refrigerant in the throttle valve is too much, that is, the refrigerant flow is too much. We usually understand that there is more fluorine, which means that more fluorine will cause low pressure.
â—† After local frosting, due to the formation of a thermal insulation layer on the surface of the evaporator, the heat exchange amount in this area is low, the expansion of the refrigerant is transferred to other areas, and the entire evaporator is frosted or frozen, and the entire evaporator is formed. The hot layer, then the expansion spreads to the compressor return pipe causing the compressor to return to the air.
If the system has a heat exchanger bypass valve, then just adjust the hot gas bypass valve, the specific method:
Open the rear end cover of the hot gas bypass valve, and then use the No. 8 Allen key to turn the adjusting nut clockwise. The adjustment process should not be too fast. Generally, pause for about half a turn to let the system run for a while and then see the frost. The situation then decides whether to continue to adjust. After the operation is stable, the compressor frosting phenomenon disappears and the end cap is tightened.
For models below 15 cubic meters, since there is no hot gas bypass valve, if the frosting phenomenon is serious, the take-off pressure of the pressure switch of the condensing fan can be appropriately adjusted. specific method:
First find the pressure switch, remove the adjustment nut of the pressure switch to fix the small piece, then use a Phillips screwdriver to rotate clockwise, the whole adjustment also needs to be carried out slowly, adjust the half turn to see the situation and then decide whether it needs adjustment.
â—† The opening of the thermal expansion valve is too large, and the temperature sensor package is incorrectly installed or loosely fixed, so that the temperature is too high and the valve core is not normally opened. The opening of the thermal expansion valve is too large, and the temperature sensor package is installed incorrectly or loosely fixed, so that the perceived temperature is too high and the valve core is abnormally opened, so that a large amount of wet steam is sucked into the compressor to cause frost at the cylinder head.
â—† When the compressor is started, the compressor is too large, or the suction shutoff valve is too open or too large.
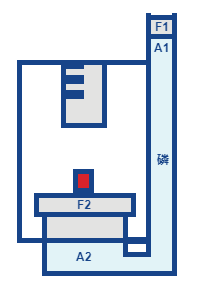
In a hydraulic press, a modest mechanical force (F1) is applied to a small area (A1). As the fluid is moved in one location, it inevitably moves elsewhere within that channel. Then a larger area (A2) generates a magnified mechanical force (F2). The force is transmitted via hydraulic pressure generated by the initial effort, F1.