Ningbo Hope Magnet Co.,Ltd , https://www.nbhpmagnet.com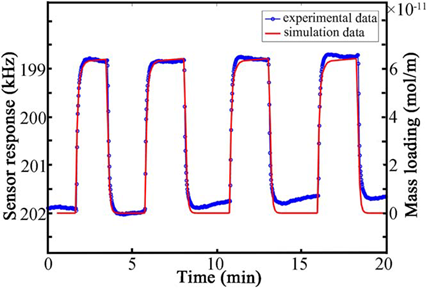
Real-time response simulation model of surface acoustic wave gas sensor established by acoustics
[ China Instrument Network Instrument Development ] In the past few decades, gas sensors have developed rapidly and played an important role in many fields. Among them, the surface acoustic wave gas sensor is widely used due to its high sensitivity, small geometric size, relatively simple device, and low production cost.
Previous studies on surface acoustic wave gas sensors have focused on the steady-state response mechanism, that is, the relationship between the gas concentration to be measured and the sensor output after reaching a long-term stable state. For the real-time response of the sensor, there is still no intuitive simulation model.
In order to describe the real-time response mechanism of surface acoustic wave gas sensors, recently, Qi Xiaolin, Ph.D. student of the Institute of Acoustics Technology, Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and his instructor Liu Jiansheng, researcher He Shitang and others have established simulation models to help visually analyze the factors affecting sensor response. Optimize sensor parameters. Relevant research results have been published in the International Journal of Applied Physics.
The researchers built models based on perturbation theory, Langmuir equations, and basic transport equations. The perturbation theory is used to describe the proportional relationship between the sensor output and the surface mass load. The Langmuir equation and the basic transfer equation are used to describe the adsorption-desorption behavior of the gas on the sensitive membrane. The mass load curve is obtained by the finite element software COMSOL.
The researchers used the prepared zinc oxide quantum dots as the sensitive membrane of the surface acoustic wave gas sensor to carry out experiments for adsorbing and desorbing dimethyl phosphate gas. The experimental results show that the gas sensor has periodicity, and the frequency response simulation curve agrees well with the experimental results.
This experiment of adsorption-desorption of gas on a SAW film is also applicable to other types of SAW gas sensors, which is beneficial to the production of higher performance surface acoustic wave gas sensors.
In the follow-up study, the researchers will use the model to analyze the factors affecting the response of the surface acoustic wave gas sensor and optimize the design of the sensor.
(Original title: Acoustic surface acoustic wave gas sensor real-time response simulation model)